Action Segmentation on Large Egocentric Cooking Dataset
The task of action segmentation involves identifying not only the start and end time of differ- ent actions in an untrimmed video but also the action types. Previous approaches take in only visual inputs, whereas our approach is the first attempt to solve the action segmentation task of a dataset as large and complex as EPIC-KITCHENS Damen et al. in the multimodal setting.. We build upon the existing MSTCN model Farha et al. which produces the start and end time of segments in a video, and we uses the visual features of the predicted segment to retrieve the closest narration in terms of their distance in the joint space. Although the video-text retrieval component does not improve baseline performance, we analyze its strength in terms of action recognition and the causes of potential failure cases.
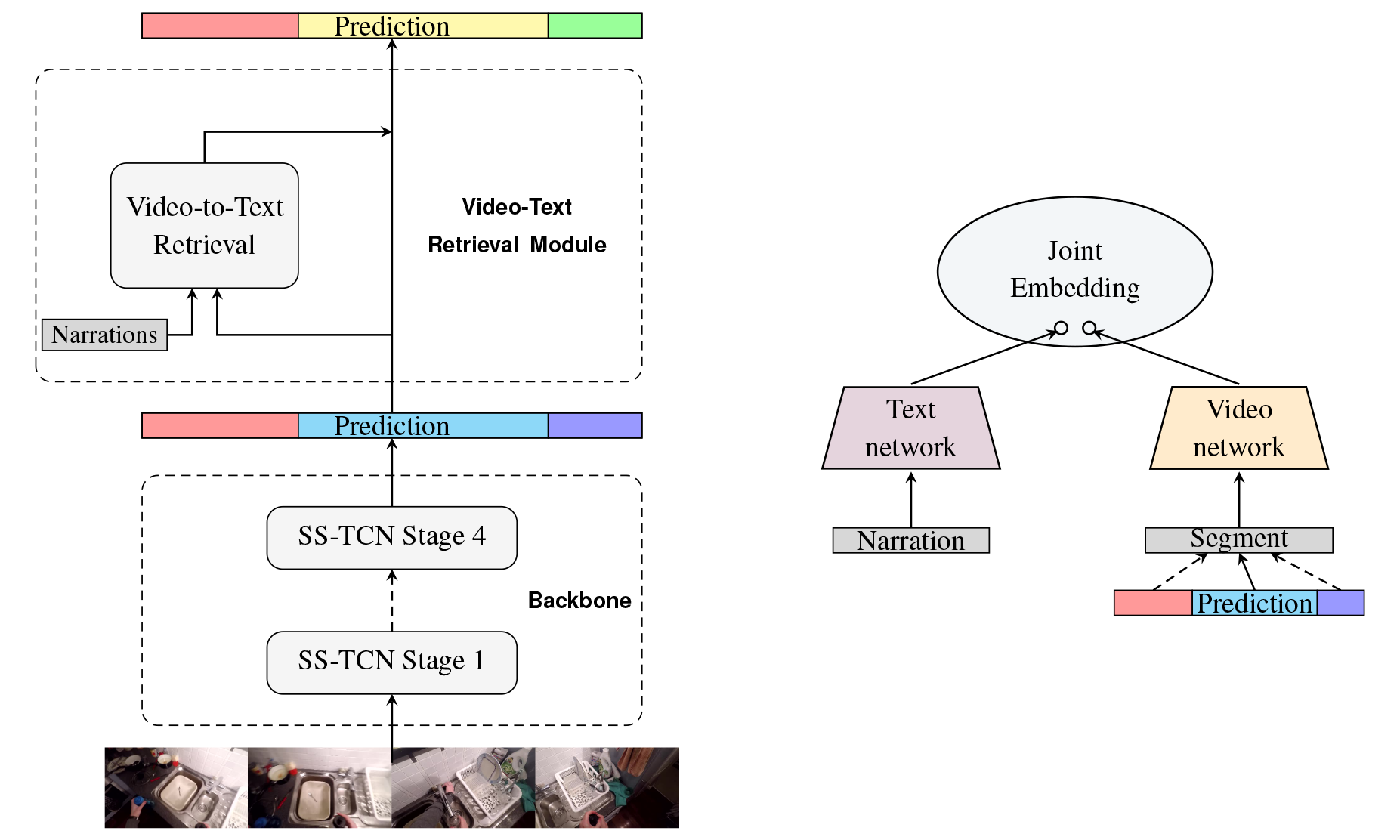
We use the original implementation of MSTCN as the backbone model and utilize an enriched, pretrained video-text embedding to improve the initial labeling from the backbone model. We extracted frame-level and video-level features similarly as in Miech et al.. We perform video-text matching between a segment and every verb by computing the cosine similarity score.
We find a strong positive correlation between richness of text and performance of retrieval. With plain verbs as label, the retrieval result is of orders of magnitudes worse than if the entire narration and its context are provided. For verbs that doesn’t correspond to a single action (e.g. take), the less ambiguous object can narrow down the search space for appropriate verbs. Furthermore, length of segments also affects performance and although text input assists in identifying the action, the quality of the visual feature is equally important in ensuring the correct retrieval.
References
- Dima Damen, Hazel Doughty, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Antonino Furnari, Jian Ma, Evangelos Kazakos, Davide Moltisanti, Jonathan Munro, Toby Perrett, Will Price, and Michael Wray. 2020. Rescal- ing egocentric vision. CoRR, abs/2006.13256.
- Y. A. Farha and J. Gall. 2019. Ms-tcn: Multi-stage tem- poral convolutional network for action segmentation. In 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages 3570–3579.
- Antoine Miech, Dimitri Zhukov, Jean-Baptiste Alayrac, Makarand Tapaswi, Ivan Laptev, and Josef Sivic. 2019. HowTo100M: Learning a Text-Video Embed- ding by Watching Hundred Million Narrated Video Clips. In ICCV.